The need and importance of extracting data from the web is becoming increasingly loud and clear. Every few weeks, I find myself in a situation where we need to extract data from the web to build a machine learning model.
For example, last week we were thinking of creating an index of hotness and sentiment about various data science courses available on the internet. This would not only require finding new courses, but also scraping the web for their reviews and then summarizing them in a few metrics!
This is one of the problems / products whose efficacy depends more on web scraping and information extraction (data collection) than the techniques used to summarize the data.In this article, you will get to learn and how to implement the Web Scarping in Python Using BeautifulSoup.
Note: We have also created a free course for this article – Introduction to Web Scraping using Python. This structured format will help you learn better.
There are several ways to extract information from the web. Use of APIs being probably the best way to extract data from a website. Almost all large websites like Twitter, Facebook, Google, Twitter, StackOverflow provide APIs to access their data in a more structured manner. If you can get what you need through an API, it is almost always preferred approach over web scraping. This is because if you are getting access to structured data from the provider, why would you want to create an engine to extract the same information.
Sadly, not all websites provide an API. Some do it because they do not want the readers to extract huge information in a structured way, while others don’t provide APIs due to lack of technical knowledge. What do you do in these cases? Well, we need to scrape the website to fetch the information.
There might be a few other ways like RSS feeds, but they are limited in their use and hence I am not including them in the discussion here.

Web scraping is a computer software technique of extracting information from websites. This technique mostly focuses on the transformation of unstructured data (HTML format) on the web into structured data (database or spreadsheet).
You can perform web scraping in various ways, including use of Google Docs to almost every programming language. I would resort to Python because of its ease and rich ecosystem. It has a library known as ‘BeautifulSoup’ which assists this task. In this article, I’ll show you the easiest way to learn web scraping using python programming.
For those of you, who need a non-programming way to extract information out of web pages, you can also look at import.io . It provides a GUI driven interface to perform all basic web scraping operations. The hackers can continue to read this article!
BeautifulSoup is a popular Python library used for parsing HTML and XML documents. It’s particularly useful for web scraping tasks. Here’s a breakdown of its key functionalities:
Web scraping involves extracting data from websites in an automated way. Here’s the typical steps involved:
As we know, Python is an open source programming language. You may find many libraries to perform one function. Hence, it is necessary to find the best to use library. I prefer BeautifulSoup (Python library), since it is easy and intuitive to work on. Precisely, I’ll use two Python modules for scraping data:
BeautifulSoup does not fetch the web page for us. That’s why, I use urllib2 in combination with the BeautifulSoup library.
Python has several other options for HTML scraping in addition to BeatifulSoup. Here are some others:
While performing web scarping, we deal with html tags. Thus, we must have good understanding of them. If you already know basics of HTML, you can skip this section. Below is the basic syntax of HTML:This syntax has various tags as elaborated below:
Other useful HTML tags are:

If you are new to this HTML tags, I would also recommend you to refer HTML tutorial from W3schools. This will give you a clear understanding about HTML tags.
Here, I am scraping data from a Wikipedia page. Our final goal is to extract list of state, union territory capitals in India. And some basic detail like establishment, former capital and others form this wikipedia page. Let’s learn with doing this project step wise step:
#import the library used to query a website
import urllib2 #if you are using python3+ version, import urllib.request#specify the url
wiki = "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_state_and_union_territory_capitals_in_India"#Query the website and return the html to the variable 'page'
page = urllib2.urlopen(wiki) #For python 3 use urllib.request.urlopen(wiki)#import the Beautiful soup functions to parse the data returned from the website
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup#Parse the html in the 'page' variable, and store it in Beautiful Soup format
soup = BeautifulSoup(page)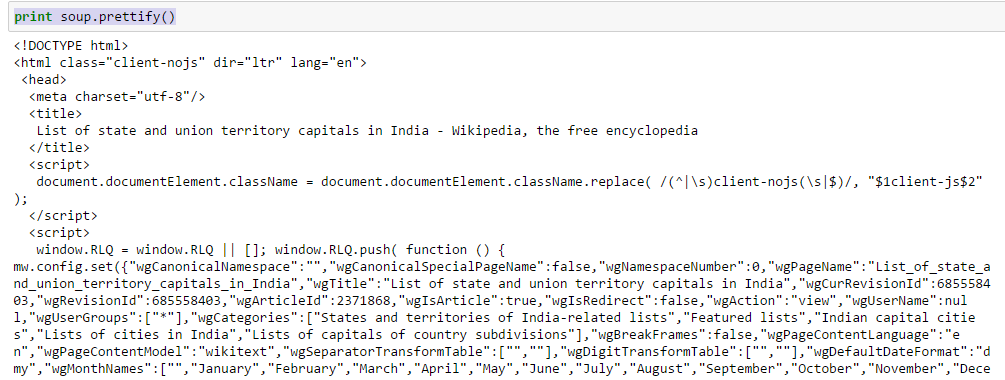 Above, you can see that structure of the HTML tags. This will help you to know about different available tags and how can you play with these to extract information.
Above, you can see that structure of the HTML tags. This will help you to know about different available tags and how can you play with these to extract information.In[30]:soup.title Out[30]:<title>List of state and union territory capitals in India - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia</title>
In [38]:soup.title.string Out[38]:u'List of state and union territory capitals in India - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia'
In [40]:soup.a Out[40]:<a id="top"></a>
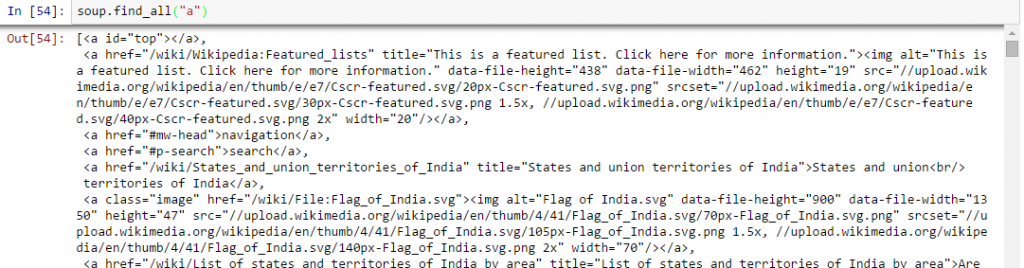
Above, you can see that, we have only one output. Now to extract all the links within <a>, we will use “find_all().
Above, it is showing all links including titles, links and other information. Now to show only links, we need to iterate over each a tag and then return the link using attribute “href” with get.
all_tables=soup.find_all('table') Now to identify the right table, we will use attribute “class” of table and use it to filter the right table. In chrome, you can check the class name by right click on the required table of web page –> Inspect element –> Copy the class name OR go through the output of above command find the class name of right table.
right_table=soup.find(‘table’, class_=’wikitable sortable plainrowheaders’) right_table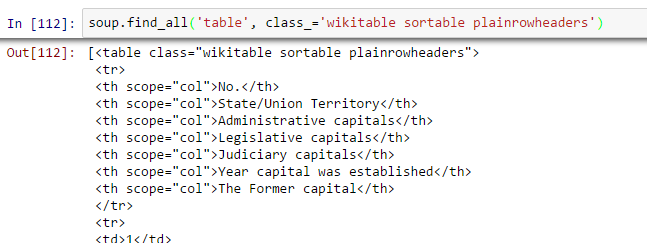 Above, we are able to identify right table.
Above, we are able to identify right table. 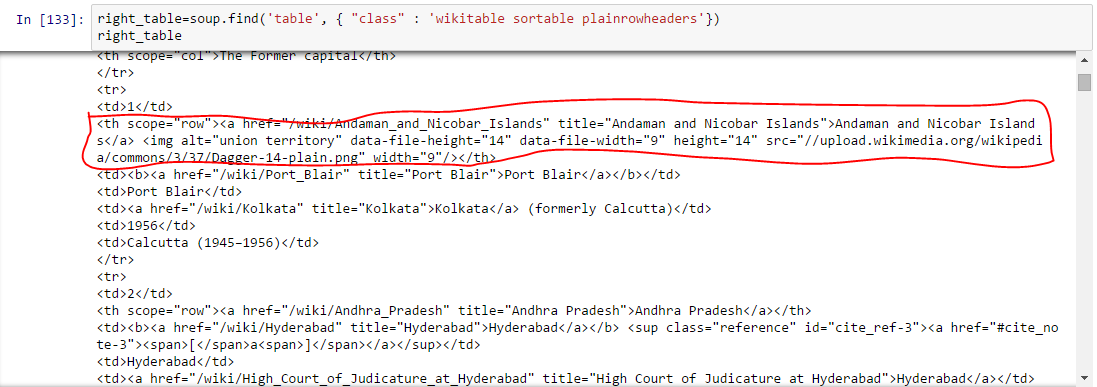 Above, you can notice that second element of <tr> is within tag <th> not <td> so we need to take care for this. Now to access value of each element, we will use “find(text=True)” option with each element. Let’s look at the code:
Above, you can notice that second element of <tr> is within tag <th> not <td> so we need to take care for this. Now to access value of each element, we will use “find(text=True)” option with each element. Let’s look at the code:#Generate lists
A=[]
B=[]
C=[]
D=[]
E=[]
F=[]
G=[]
for row in right_table.findAll("tr"):
cells = row.findAll('td')
states=row.findAll('th') #To store second column data
if len(cells)==6: #Only extract table body not heading
A.append(cells[0].find(text=True))
B.append(states[0].find(text=True))
C.append(cells[1].find(text=True))
D.append(cells[2].find(text=True))
E.append(cells[3].find(text=True))
F.append(cells[4].find(text=True))
G.append(cells[5].find(text=True))#import pandas to convert list to data frame
import pandas as pd
df=pd.DataFrame(A,columns=['Number'])
df['State/UT']=B
df['Admin_Capital']=C
df['Legislative_Capital']=D
df['Judiciary_Capital']=E
df['Year_Capital']=F
df['Former_Capital']=G
df
Finally, we have data in dataframe:
Similarly, you can perform various other types of web scraping using “BeautifulSoup“. This will reduce your manual efforts to collect data from web pages. You can also look at the other attributes like .parent, .contents, .descendants and .next_sibling, .prev_sibling and various attributes to navigate using tag name. These will help you to scrap the web pages effectively.-
Now, if you know regular expressions, you might be thinking that you can write code using regular expression which can do the same thing for you. I definitely had this question. In my experience with BeautifulSoup and Regular expressions to do same thing I found out:
So, it boils down to speed vs. robustness of the code and there is no universal winner here. If the information you are looking for can be extracted with simple regex statements, you should go ahead and use them. For almost any complex work, I usually recommend BeautifulSoup more than regex.
In this article, we looked at web scraping methods using “BeautifulSoup” and “urllib2” in Python. We also looked at the basics of HTML and perform the web scraping step by step while solving a challenge. I’d recommend you to practice this and use it for collecting data from web pages.
Did you find this article helpful? Please share your opinions / thoughts in the comments section below.
Note: We have also created a free course for this article – Introduction to Web Scraping using Python. This structured format will help you learn better.
If you like what you just read & want to continue your analytics learning, subscribe to our emails, follow us on twitter or like our facebook page.
1. Install BeautifulSoup: pip install beautifulsoup4
2. Use it to parse HTML content and extract data.
3.Example code:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = ‘https://example.com’
response = requests.get(url)
html_content = response.content
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, ‘html.parser’)
links = soup.find_all(‘a’)
for link in links:
print(link.get(‘href’))
1.”BS4″ stands for BeautifulSoup version 4, the latest version of the library.
2.BeautifulSoup is a Python library for web scraping.
3.It simplifies parsing HTML and XML to extract desired data.
1.BeautifulSoup is widely used and user-friendly.
2. Whether it’s the best depends on the project needs.
3.Other options like Scrapy, lxml, and Selenium also suit specific requirements. Choose based on project complexity and preferences.
Scrapy vs BeautifulSoup:
Simple project/learning? BeautifulSoup (easy to use).
Large project/complex scraping? Scrapy (powerful framework).pen_spark
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit,
Hi Sunil, Thanks for such a great article. I am new in data science area but you people make me confident to be a good analyst. Carry on.
Thank you for the article! I am taking an online course and was looking all over the web to understand Beautiful Soup. I find your article most helpful.
Hi, I tried to complete this work with Python 2.7.10, Pycharm and ipython notebook. All my efforts failed for soup =BeautifulSoup(page) ipython error : IncompleteRead python 2.7 and Pycharm error : TypeError: 'module' object is not callable What to do ? Please help
Hi Mohammad try the below code ,it should work soup =BeautifulSoup.BeautifulSoup(page). Regards, Naveen
you need to install Beautifulsoup package index
thank you!
Hi Sunil, Nice explanation it helped me understand more about data scraping through python. Just a little update I don't know whether it's some version issue or something else. You 've mentioned "find_all" in the script, which when I ran has thrown an error, after exploring more on the web I found "findAll" (underscore removed and A in caps) which worked for me. Thanks
Excellent Article. Very concise, thorough and simple to understand. I would greatly appreciate other examples of grabbing data from a website and displaying results in a dataframe ( table )... If it's not too much of an inconvenience, could you provide example similar to above for obtaining best gasoline / petroleum prices in a particular region or at least point us to some good reference material? I just have to figure out how to get pandas installed on my windows 8.1 system. I installed portable python, which is basically running python from a folder. Guess I'll have to download pandas into that folder similar to how I did BeautifulSoup4. Thanks again...
Thanku for this informative blog post. I liked it so much.
Nice article , thanks for the effort
Very good article, easy to understand.
Thank you for the great article. Can you please make or suggest some tutorial on how to use API to extract data from websites like twitter and perform sentiment analysis?
Now it's my habit to learn a one small thing from AV, Indeed thanks for great to learn in this article
That's a very precise and neat article,Learnt basic knowledge about beautiful soup
Nice Article!! Beautifulsoup vs regex anology: web content is like money in a digital vault. Beautiful soup is a clean and process driven way of opening the vault door. Whereas, regex way is like breaking that door with a hammer!! Both are good. I somehow prefer the hammer way.
Great list of plugins friend. The Tables still serve a purpose. Although in the era of responsive sites it is a must have to be able to display tables responsively. League Table looks great! Definitely look into this and it has come at the right time as I am working on a site to list statistics and a table like this will work perfectly.
Really nice exercise! Thank you
Very good article. I would add a note about Selenium. I like to use Selenium and Beautiful Soup together though they overlap in functionality. Selenium can click through webpage, submit passwords, and extract data but Beautiful Soup much easier to use...together they work very well for multiple use cases.
Simply awesome! Great help! Thank you so much.
Excellent, to the point article!
simply awesome....big thanks ..keep posting
Excellent article Sunil. It was simple enough for someone like me who has very basic html knowledge to implement.
This was a great article! As a beginner to web scraping you explained everything very well. Thanks for sharing!
great one
very nice article for beginner
Very nice and easy. However, doesn't it work for Python3?
A good one
Nice post
Hi, Thanks for the useful page. Sorry if this is dumb, but do we write all this in our Jupyter books ( I am using Anaconda for Piton 2.7.12 )
Skype has launched its online-centered buyer beta for the world, after establishing it generally within the Usa and You.K. earlier this four weeks. Skype for Online also now facilitates Chromebook and Linux for immediate text messaging connection (no video and voice but, these call for a connect-in installing). The expansion of your beta adds help for a longer selection of dialects to help you bolster that international user friendliness
Hi Sunil , your articles has helped alot in understanding the concept better . i have some doubts that i would like to ask you , as i use writing code to scrap data from my twitter account and its basically that i want to list the number of follower i have , till 'soup.a' it is working fine but after that i m not able to identify which tag to use . please help !!
Thanks for the wonderful resource! Though I'd recommend using python's 'requests' library as opposed to urllib2 - it is more up-to-date and easier to use in my opinion! This is by far my favorite site on the web!!
It's a big great article, thnk you.
Hi Sunil , I could replicate same code in my environment , it was my first successful web scrapping practice , after this example i am sure i would be able same logic at many places. Thanks for your efforts and helping us to learn it in very simple and easy way..
It turn out to be a great help for me Thank you : )
Excellent Article and easy to understand!!
Very nice article, I tried as it is but i'm not getting tile tag i.e soup.title, Please help me
have you guys tried phpleafnode? the act of web scraping is to get visible contents found on web site. These contents are mostly displayed by Leaf nodes. Hence people need not stress themselves to initially find the position of the elements to get rules. To leverage these difficulties, phpleafnode is built. PHPLeafNode will accept your html and give you the leaf nodes in array form. it can be extended to do auto pattern recognition for you from which you can omit array indexes you think the values are unneeded. and the needed array indexes gets your expected values. Phpleafnode can be downloaded from github.
Hi, Thank you so much for posting this. I really appreciate your work. Keep it up. Great work!
Thank you! It was really clear and helpful! Craving to learn more here =)
how about scrapy? which one you prefer scrapy or beautiful soup? could you give me a calrity?
Really helpful...Thanks much!!!
Thanks a ton guys!!!
Can anyone help me to find a particular paragraph with a heading, from multiple web pages having same heading available?
Hi, Yes, you can use beautifulSoup to get this done. First, you have to understand Document Object Model (DOM). Find the source code of the page by right clicking on the webpage and select source code. Here you could look what is the id or class of heading you want to parse. Later you can parse it using the following code. soup = BeautifulSoup('
') soup.find_all("h2", class_="CLASSNAME")which text editor you have to used for this whole code execution like import, and other
Hi, Jupyter notebook is used in this article.